How to detect, enable and disable SMBv1, SMBv2, and SMBv3 in Windows
Источник: здесь
Источник 2: https://remontka.pro/0x80004005-unspecified-network-error/
Disabling SMBv2 or SMBv3 for troubleshooting
We recommend keeping SMBv2 and SMBv3 enabled, but you might find it useful to disable one temporarily for troubleshooting. For more information, see How to detect status, enable, and disable SMB protocols on the SMB Server.
In Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, and Windows Server 2012, disabling SMBv3 deactivates the following functionality:
- Transparent Failover - clients reconnect without interruption to cluster nodes during maintenance or failover
- Scale Out - concurrent access to shared data on all file cluster nodes
- Multichannel - aggregation of network bandwidth and fault tolerance if multiple paths are available between client and server
- SMB Direct - adds RDMA networking support for high performance, with low latency and low CPU use
- Encryption - Provides end-to-end encryption and protects from eavesdropping on untrustworthy networks
- Directory Leasing - Improves application response times in branch offices through caching
- Performance Optimizations - optimizations for small random read/write I/O
In Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2, disabling SMBv2 deactivates the following functionality:
- Request compounding - allows for sending multiple SMBv2 requests as a single network request
- Larger reads and writes - better use of faster networks
- Caching of folder and file properties - clients keep local copies of folders and files
- Durable handles - allow for connection to transparently reconnect to the server if there's a temporary disconnection
- Improved message signing - HMAC SHA-256 replaces MD5 as hashing algorithm
- Improved scalability for file sharing - number of users, shares, and open files per server greatly increased
- Support for symbolic links
- Client oplock leasing model - limits the data transferred between the client and server, improving performance on high-latency networks and increasing SMB server scalability
- Large MTU support - for full use of 10 Gigabit Ethernet (GbE)
- Improved energy efficiency - clients that have open files to a server can sleep
The SMBv2 protocol was introduced in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, while the SMBv3 protocol was introduced in Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012. For more information about SMBv2 and SMBv3 capabilities, see the following articles:
How to remove SMBv1 via PowerShell
Here are the steps to detect, disable and enable SMBv1 client and server by using PowerShell commands with elevation.
Note
The computer will restart after you run the PowerShell commands to disable or enable SMBv1.
Detect:
PowerShellGet-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName SMB1ProtocolDisable:
PowerShellDisable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName SMB1ProtocolEnable:
PowerShellEnable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName SMB1Protocol
Tip
You can detect SMBv1 status, without elevation, by running: Get-SmbServerConfiguration | Format-List EnableSMB1Protocol.
Windows Server 2012 Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2019: Server Manager method
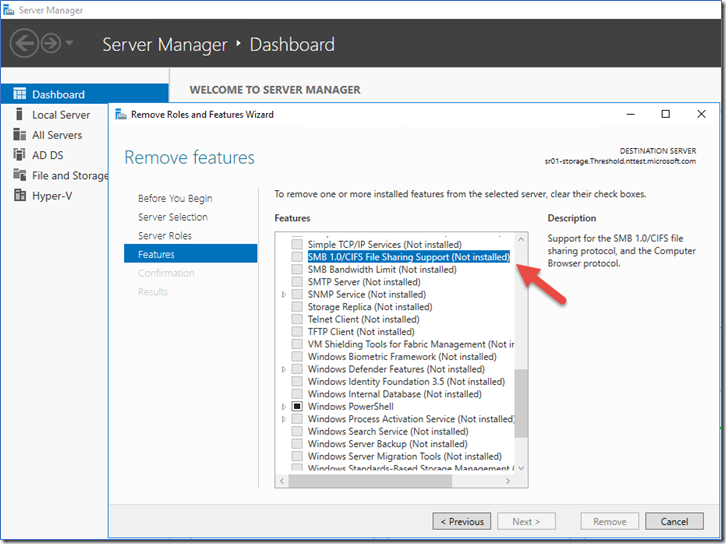
To remove SMBv1 from Windows Server:
- On the Server Manager Dashboard of the server where you want to remove SMBv1, under Configure this local server, select Add roles and features.
- On the Before you begin page, select Start the Remove Roles and Features Wizard, and then on the following page, select Next.
- On the Select destination server page under Server Pool, ensure that the server you want to remove the feature from is selected, and then select Next.
- On the Remove server roles page, select Next.
- On the Remove features page, clear the check box for SMB 1.0/CIFS File Sharing Support and select Next.
- On the Confirm removal selections page, confirm that the feature is listed, and then select Remove.
Windows 8.1, Windows 10, and Windows 11: Add or Remove Programs method
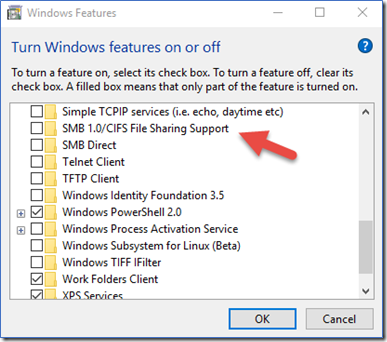
To disable SMBv1 for the mentioned operating systems:
- In Control Panel, select Programs and Features.
- Under Control Panel Home, select Turn Windows features on or off to open the Windows Features box.
- In the Windows Features box, scroll down the list, clear the check box for SMB 1.0/CIFS File Sharing Support and select OK.
- After Windows applies the change, on the confirmation page, select Restart now.
How to detect status, enable, and disable SMB protocols
Note
When you enable or disable SMBv2 in Windows 8 or Windows Server 2012, SMBv3 is also enabled or disabled. This behavior occurs because these protocols share the same stack.
Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 introduced the new Set-SMBServerConfiguration Windows PowerShell cmdlet. The cmdlet enables you to enable or disable the SMBv1, SMBv2, and SMBv3 protocols on the server component.
You don't have to restart the computer after you run the Set-SMBServerConfiguration cmdlet.
SMBv1
Detect:
PowerShellGet-SmbServerConfiguration | Select EnableSMB1ProtocolDisable:
PowerShellSet-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB1Protocol $falseEnable:
PowerShellSet-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB1Protocol $true
For more information, see Server storage at Microsoft.
SMB v2/v3
Detect:
PowerShellGet-SmbServerConfiguration | Select EnableSMB2ProtocolDisable:
PowerShellSet-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB2Protocol $falseEnable:
PowerShellSet-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB2Protocol $true
For Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Vista, and Windows Server 2008
To enable or disable SMB protocols on an SMB Server that is running Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Vista, or Windows Server 2008, use Windows PowerShell or Registry Editor.
Additional PowerShell methods
Note
This method requires PowerShell 2.0 or later.
SMBv1 on SMB Server
Detect:
Get-Item HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters | ForEach-Object {Get-ItemProperty $_.pspath}
Default configuration = Enabled (No registry named value is created), so no SMB1 value will be returned
Disable:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters" SMB1 -Type DWORD -Value 0 -Force
Enable:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters" SMB1 -Type DWORD -Value 1 -Force
Note You must restart the computer after you make these changes. For more information, see Server storage at Microsoft.
SMBv2/v3 on SMB Server
Detect:
Get-ItemProperty HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters | ForEach-Object {Get-ItemProperty $_.pspath}
Disable:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters" SMB2 -Type DWORD -Value 0 -Force
Enable:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters" SMB2 -Type DWORD -Value 1 -Force
Note
You must restart the computer after you make these changes.
Registry Editor
Important
Follow the steps in this section carefully. Serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly. Before you modify it, back up the registry for restoration in case problems occur.
To enable or disable SMBv1 on the SMB server, configure the following registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters
Registry entry: SMB1
REG_DWORD: 0 = Disabled
REG_DWORD: 1 = Enabled
Default: 1 = Enabled (No registry key is created)
To enable or disable SMBv2 on the SMB server, configure the following registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters
Registry entry: SMB2
REG_DWORD: 0 = Disabled
REG_DWORD: 1 = Enabled
Default: 1 = Enabled (No registry key is created)
Note
You must restart the computer after you make these changes.
Disable SMBv1 by using Group Policy
This section introduces how to use Group Policy to disable SMBv1. You can use this method on different versions of Windows.
SMBv1
This procedure configures the following new item in the registry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters
- Registry entry: SMB1
- REG_DWORD: 0 = Disabled
To use Group Policy to configure this, follow these steps:
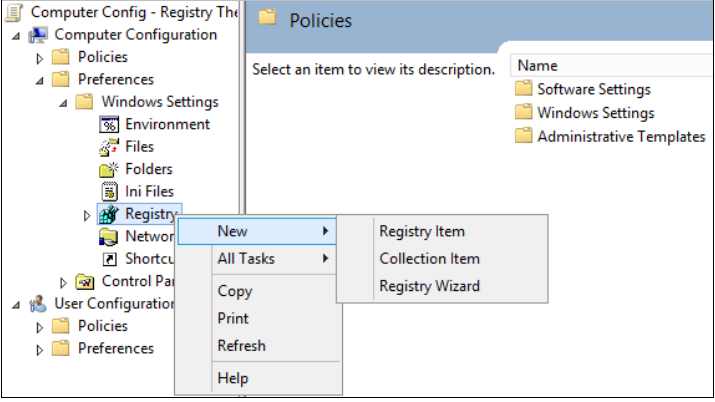
Open the Group Policy Management Console. Right-click the Group Policy object (GPO) that should contain the new preference item, and then click Edit.
In the console tree under Computer Configuration, expand the Preferences folder, and then expand the Windows Settings folder.
Right-click the Registry node, point to New, and select Registry Item.
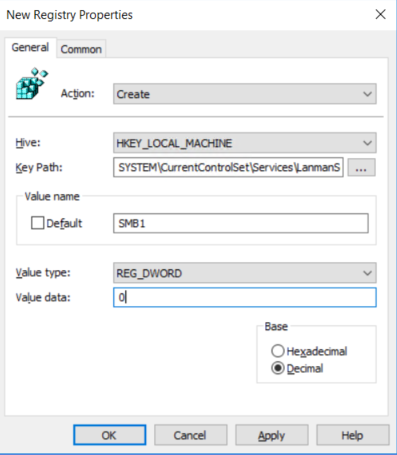
In the New Registry Properties dialog box, select the following:
- Action: Create
- Hive: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
- Key Path: SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters
- Value name: SMB1
- Value type: REG_DWORD
- Value data: 0
This procedure disables the SMBv1 Server components. This Group Policy must be applied to all necessary workstations, servers, and domain controllers in the domain.
Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий